Are Bed Bugs Dangerous? Bed bugs are not typically dangerous but can cause itching, discomfort, and anxiety due to their presence and bites.
Bed bugs disrupt sleep and can cause skin irritation, impacting both comfort and appearance with their itchy bites.
Bed bugs have made an unwelcome comeback in many countries over the last two decades.
These tiny, blood-sucking pests can transform a restful night’s sleep into a nightmare of constant itching and scratching. But beyond being a nuisance, are bed bugs dangerous? This article will explore the health risks posed by these insects.
What Are Bed Bugs?
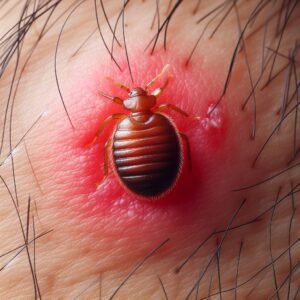
Bed bugs (Cimex lectularius) are small, flat, parasitic insects that feed solely on the blood of people and animals while they sleep. An adult bed bug reaches 5mm in length and has a red-brown coloration.
Unfed bed bugs are flat, allowing them to hide easily in tiny crevices in mattresses, bed frames, furniture, and even suitcases. After feeding, they swell up with blood, developing a dark red color.
Bed bugs were nearly eradicated in many industrialized countries due to the widespread use of potent pesticides like DDT in the mid 20th century.
But thanks to several factors like increased global travel, bans on toxic chemicals, and bed bug resistance to pesticides, these insects have made a dramatic resurgence globally since the late 1990s.
Are Bed Bug Bites Dangerous?
The main way that bed bugs impact human health is through their bites, which can cause skin irritation and itching. An estimated 20-50% of people do not react noticeably to bed bug bites and show no symptoms at all.
Those who do react have reactions ranging from slight red marks that disappear quickly to large, itchy skin welts that may take over a week to heal.
Some people may also have allergic reactions to the anesthetic and anticoagulant chemicals bed bugs inject when they bite, resulting in severe inflammation, rashes, blisters, or scarring.
Excessive scratching of bed bug bites can rupture the skin and increase the risk of infection, especially among vulnerable people like infants, the elderly, or those with autoimmune disorders.
Related post 12 Bed Bug Myths Debunked: Separating Fact from Fiction
Some minor skin infections like impetigo or ecthyma may result. Overall though, bed bug bites pose a relatively low health risk and are seldom dangerous on their own unless an individual has numerous repeated exposures.
Do Bed Bugs Transmit Disease?
Whether bed bugs can transmit disease to humans is still an open question. Based on current evidence, public health organizations say these insects are unlikely to transmit human pathogens under natural conditions.
But recent research paints a more complicated picture regarding diseases like MRSA, Hepatitis B, and Chagas disease:
MRSA and Hepatitis B
Multiple studies have detected methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bacteria and Hepatitis B Virus DNA in bed bugs.
However, few studies examine whether live human pathogens are actually present or can be transmitted via bites. One early study found bed bugs incapable of transmitting the Hepatitis B Virus despite carrying its genetic material. Overall transmission risk is unclear.
Chagas Disease
Certain insects vectors can transmit Trypanosoma cruzi parasite between infected humans via fecal contamination. A new study did detect viable T. cruzi parasites in bed bugs up to 18 days after feeding on infected mice.
Another study found bed bugs that had fed on infected humans were not able to transmit T. cruzi parasites afterward. Again, the evidence remains inconclusive and indicates more research is needed. Public health agencies maintain bed bugs are still unlikely vectors for Chagas disease.
Are bed bugs dangerous? The Nuisance Factor of Bed Bugs
Beyond the direct physical dangers posed by bed bug bites, these stubborn pests can create enormous distress via their persistent, hard-to-eliminate infestations. Some aspects that make them so problematic include:
Annoying and Disruptive Bites
While bed bug bites do not transmit disease, they can make your nights (or days) a living hell. Unlike fleas or mosquitoes which feed quickly, bed bugs bite slowly and repeatedly.
A female may bite a single human 300 times over its lifespan! This causes relentless itchy welts that prevent continuous sleep and torment victims for days or weeks after exposure.
Stigma and Helplessness
The social stigma around bed bugs means those suffering from infestations may avoid telling family or friends.
The feeling that bugs are crawling all over their furniture and beds can be isolating. The helplessness around eliminating the expensive bed bug scourge without professional pest control further piles on distress.
Anxiety and Phobias
Studies show that having bed bugs leads to increased anxiety, insomnia and phobias about insects. About 1/3 of those living in infested homes report anxiety and insomnia serious enough to disrupt their daily lives.
Living in constant stress has negative impacts both physically and psychologically. Extreme cases may get Post Traumatic Stress Disorder after enduring bed bug problems.
Financial Burden
Dealing with bed bugs is incredibly expensive for homeowners. Getting professional extermination services can run into thousands of dollars and is often not covered by insurance.
For lower-income families or cash-strapped city councils managing bed bugs in public housing or shelters, the costs are major financial blows. Repeated bed bug infestations only have multiple costs for victims.
Broader Health and Societal Impacts
Beyond individual homeowners, bed bug infestations also negatively impact society in various ways:
1. Overuse of Dangerous Pesticides
Both professional pest control services and desperate homeowners often misuse toxic insecticides in trying to battle bed bugs.
Foggers, dust, and sprays containing concentrated amounts of permethrin, DDVP, pyrethrins, mnemonics, and other chemicals put residents and pets at risk of poisoning.
Long-term exposure to traces of these pesticides could potentially affect our endocrine or reproductive systems too.
2. Burden on Vulnerable Groups
Bed bug infestations disproportionately impact marginalized groups like the homeless, mentally ill, and elderly who lack resources for professional bed bug detection and removal.
Municipal shelters struggle with controlling outbreaks that spread quickly in crowded living conditions. Low-income households including urban public housing face high costs when trying to eliminate pests.
3. Loss of Tourism/Business Revenues
Hotels and apartments with bed bugs face backlash in the age of online reviews spreading news of problems widely.
Bed bug lawsuits over bites or reputational damage regularly target the hospitality industry. US cities lose millions in tourism and tax revenues from visitors avoiding locations with rampant bed bug problems in hotels. Nobody wants to bring back unwanted blood-sucking souvenirs from vacation.
Is it dangerous to sleep with bed bugs?
Sleeping with bed bugs isn’t directly dangerous, but their presence can lead to discomfort, itching, and skin irritation from their bites. Furthermore, constant exposure may cause psychological distress. While they don’t transmit diseases, their presence can negatively impact mental and physical well-being, requiring prompt eradication measures.
Can bed bugs affect your health?
Bed bugs can impact health by causing skin irritation, allergic reactions, and psychological distress due to their presence and bites. While they don’t transmit diseases, their effects can lead to discomfort and anxiety, affecting overall well-being and quality of life.
What happens if a bed bug bites you?
When a bed bug bites you, it injects saliva containing anesthetic and anticoagulant compounds, causing redness, itching, and swelling at the bite site. Some individuals may develop allergic reactions or secondary skin infections from scratching.
Can you be killed by bed bugs?
No, bed bugs cannot directly kill you. While their bites can cause discomfort and potential allergic reactions, they do not transmit diseases or pose a lethal threat to humans.
Conclusion
Bed bugs may not directly cause infectious disease, but they undoubtedly negatively impact human health, whether it’s through bothersome bites, mental health issues or misuse of pesticides.
These pests are easily spread through travel and can catastrophically drive up costs for homeowners or cash-strapped municipalities trying to manage infestations.
While bed bugs themselves pose a low individual health risk physically, their persistence and the scale of ongoing infestations is concerning for populations worldwide.
Public health authorities must allocate more efforts to educate vulnerable communities on prevention and implement bed bug monitoring to contain outbreaks, especially as these unwelcome pests continue to evolve pesticide resistance.