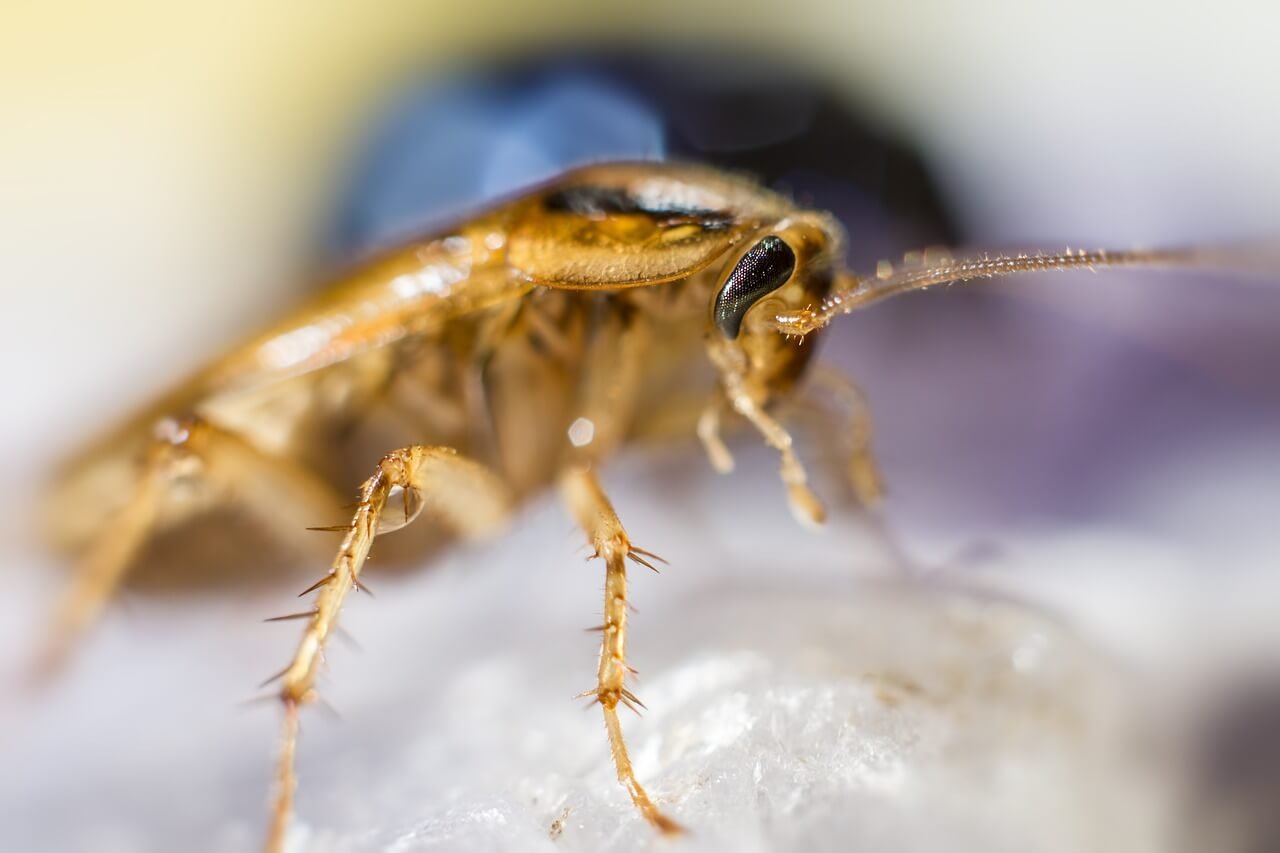
German vs American Cockroach: Finding roaches in your home can be an unpleasant surprise and a worrying sign of an infestation.
Two species – the German cockroach and the American cockroach – frequently become unwelcome residents. While they share similarities, understanding key differences in the biology and behavior of German vs American cockroaches can optimize removal and prevention strategies.
Read on to learn how to identify these cockroach varieties, why they invading our homes, effective methods for eliminating current infestations, and tips to prevent cockroaches from taking up residence again.
Identifying Key Differences Between German VS American Cockroaches
German and American cockroaches have distinct appearances and habitat preferences that enable identification. Knowing a few key biological differences will also inform control plans tailored to each species.
Physical Differences Size and markings offer simple ways to tell German roaches apart from their American counterparts. Knowing preferred foods, shelters, reproductive capabilities, and patterns of activity also facilitates targeted management.
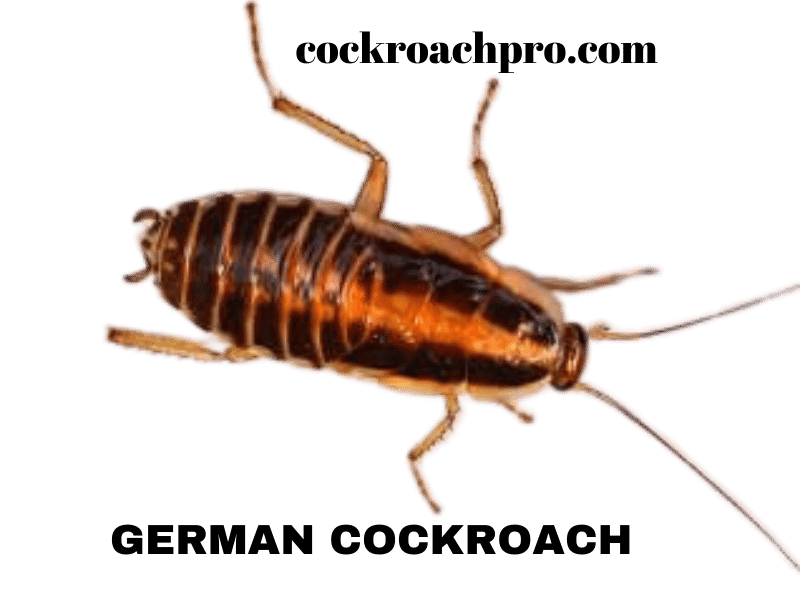
Appearance and Size German cockroaches have two dark stripes running horizontally along their pronotum, the upper shell-like structure behind the head. These stripes resemble a captain’s bars, earning them the nickname “two-striped cockroaches.” Adults measure 1⁄2 to 5⁄8 inches long with light-brown bodies and darker-hued wings.

American cockroaches are much larger at 1 1⁄2 to 2 inches long as adults. Solid reddish-brown, they lack the distinctive striping of German cockroaches. The pronotum of an American cockroach wraps around the head with a lighter-colored edge.
Preferred Foods & Habitats
German cockroaches prefer starchy foods and sweets inside moist, warm indoor spaces like kitchens and bathrooms. They primarily live indoors, hiding near plumbing fixtures and appliances.
American roaches exhibit more variety in their shelters and diet. They thrive outdoors eating decaying organic matter but will also consume some human foods. Indoors, they are also drawn to moist areas like pipes and drains.
Reproduction & Lifecycle
A German cockroach female produces an egg case holding 30 to 40 eggs on average and can generate 4 to 8 egg cases in her lifetime. Development from eggs to reproductive adults spans about 100 days on average.
American roach females produce egg cases that each hold around 16 young. But they remain reproductive for several years and generate up to 90 egg cases altogether resulting in substantially higher lifetime reproduction. It takes around 600 days for American roaches to complete development.
Activity Patterns
German cockroaches hide in dark crevices and avoid light, earning them the label of “nocturnal.” They venture out mostly at night to seek food and water sources along their shelter paths.
American roaches exhibit more flexible activity patterns. They often seek food at night but will roam around exposed areas during the daytime as well. Overall, American cockroaches travel greater distances from their core shelters than German cockroaches.
Why Cockroaches Invade Our Homes
German and American cockroaches become household pests mainly when seeking necessities like food, water, warmth, and shelter. Indoors offers a perfectly balanced ecosystem for these scavenging insects. Understanding exactly what they gain from our living spaces facilitates removal by taking away key attractions.
Seeking Food & Water
Cockroaches have simple survival needs – if they gain access, indoor environments provide ideal temperature, hydration, and abundant food sources. They are drawn to food debris, grease accumulation, sweet substances, starchy foods, and moist areas like sinks and drains. Avoiding kitchen and bathroom clutter and spills disrupts their ability to thrive.
Human homes concentrate on robust food opportunities compared to natural settings. Whether noshing on our leftovers or scraping up tiny crumbs, cockroaches enjoy a perfect feeding ground in our houses. Cutting off food access is paramount in elimination and prevention.
Entry for Shelter & Warmth
Cockroaches gravitate to indoor shelters offering small cracks, gaps, and hard-to-reach voids with moderate temperature and humidity. Kitchen cabinets, wall voids, attics, and subfloors provide ideal harborage.
They also cluster around heat sources like appliances and pipes that radiate warmth. Sealing off these attractions removes the extended habitat benefiting populations.
Why They Keep Coming Back?
Cockroaches are masters at fitting through astonishingly small spaces and gaps in siding, utility lines, and structures. If they gain entry at all, they can rapidly build colonies and breed recurrent generations.
They detect and follow pheromone trails to food, water, and gathering spots. Once an area is tagged by roach scent markers, they will return en mass unless deterrents disrupt trails. This is why thorough elimination combined with preventive measures is essential for long-term relief from recurring household infestations.
8 Tips for Getting Rid of Cockroaches
When confronted with roaches, take immediate and thorough action to mitigate proliferation. A combination of approaches works best to eliminate populations completely.
1. Inspect and Identify Entry Points
Conduct thorough visual checks around all rooms to identify cracks or voids allowing entry from outdoors. Target exterior barriers first in removal plans. Identify problem areas like unused drains, gaps around pipes, and tiny crevices capable of admitting German cockroaches.
2. Remove Food, Water & Clutter
Eliminate free meals by cleaning all floors and surfaces completely. Store all food in sealed containers so crumbs and spills offer no attraction. Fix any plumbing leaks and dry out moist areas. Remove stacks of clutter blocking access behind appliances and shelving.
3. Apply Boric Acid Powder
Boric acid powder kills roaches slowly but surely through ingestion and contact. Focus first along sheltered travel paths indoors like wall voids, cracks, and crevices where colonies hide and breed. Apply lightly into drains, around appliances, and under sinks. The key is getting the powder where roaches traverse and congregate.
4. Use Gel Baits
Insecticide gel baits offer both a food attractant and a toxin for controlling roaches. Place tiny drops or precision bait stations along walls, the backs of cabinets, under appliances, and other areas with observed activity. Maintain baits according to label directions, refreshing monthly. Rotate active ingredients to avoid bait aversion.
5. Monitor with Sticky Traps
Traps monitor movement and gauge the effectiveness of removal efforts. Place traps against interior walls around plumbing hardware in kitchens and bathrooms. Check and replace traps weekly while reducing roach populations. Look for changes in activity levels and life stages caught.
6. Apply Insect Growth Regulator Products
Insect growth regulator (IGR) products disrupt the roach life cycle, preventing successful molting and reproduction. Combining IGR treatments with bait stations, traps, and boric acid maximizes population decline. Focus IGR application points to concealed areas around pipes, appliances, and wall voids.
7. Vacuum Egg Cases & Reduce Harborage
Vacuuming physically removes egg cases and limits potential population spread. Use crevice tools to systematically vacuum voids around appliances, cabinet corners, attics, and sub-floor cracks. Eliminating clutter reduces harborage areas indoors as well.
8. Consider Professional Pest Control
For severe infestations across multiple rooms, professional pest control concentrates experience and chemical options for stubborn populations. Qualified exterminators have access to stronger insecticides to purge multi-room infiltrations. They also identify and seal key entry points.
7 Tips for Preventing Roaches from Returning
Prevent future infestations by adhering to sanitation basics and conducting routine monitoring. Follow integrated pest management guidelines endorsed by professional exterminators.
1. Eliminate Food Sources
Store all pantry items in airtight containers. Clean dishes and empty garbage receptacles daily. Wipe up spills and crumbs immediately. Take the trash out regularly. Eliminate pet food bowls overnight. Remove recyclables promptly. Compost food scraps securely outdoors only.
2. Fix Plumbing Leaks
Repair any water leaks or moisture sources. Keep drains protected and functional. Eliminate standing water and condensation which can attract roaches. Dehumidify excessively damp basements or crawl spaces.
3. Take Out Trash Regularly
Garbage contains food waste roaches feast upon. Take bags out daily tying off tightly. Use bins with self-closing lids lined with plastic bags. Coordinate regular waste removal services for larger refuse items.
4. Store Food in Sealed Containers
Deny roaches tempting leftovers by keeping everything in tightly sealed glass, plastic or metal containers. This removes odors luring many insects as well.
5. De-Clutter Hiding Places
Cockroaches covet household clutter piled along walls, crammed in cabinets and blocking access behind appliances. Organize storage areas, maintain accessibility for cleaning and vacuum behind furniture items. Reduce available harborage sites.
6. Seal Cracks & Crevices
Plug and seal any cracks or voids with caulk both indoors and outside along foundation edges. Screen drain pipes and openings appropriately. Weather strip around doors and windows to deny entry access. Eliminate gaps around pipe penetrations.
7. Monitor & Act Fast If Seen
Deploy sticky traps routinely to detect early stage activity, particularly German cockroaches. Focus trapping areas in likely infiltration spots like kitchens and bathrooms.
Implement control measures immediately at the first signs of returning cockroaches. Set traps outdoors to determine if populations are developing near building foundations as well.
Conclusion
Academic estimates indicate up to 4 species of cockroach take up residence in human households globally. German cockroaches and American cockroaches dominate as the most prolific domestic pest varieties. Understanding key differences between them facilitates strategic management plans tailored to their respective behaviors and biology.
Cutting off food resources and access to indoor shelters provides the cornerstones for eliminating current infestations in residences and preventing new ones from developing. Americans spend an estimated $2 billion annually trying to control cockroaches using largely reactive measures. Shifting focus toward proactive, preventive steps offers more effective disruption of conditions sustaining roach populations long-term.
With attention to entry barriers, sanitation, and monitoring, homeowners can achieve lasting relief from these unhygienic insects we commonly battle in our living environments. Consistently restricting what German and American cockroaches need to thrive and reproduce behind our walls wins the war against future invasions.




